J. JAYAPANDIAN
IGCAR, Material Science Div., Kalpakkam. PIN 603102, Tamil Nadu, India;
fax: 0091-04114-40360; e-mail: msd@igcar.ernet.in.
ELECTRONIC DESIGN / MAY 27, 1997から引用
I
n many linear applications of field-effect transistors, the FET is used as a
constant-current device for large
VDS (i.e., drain-to-source voltage) or as
ohmic resistance for small VDS. In the
region before pinch-off, the FET is effective as a voltage-variable resistor.
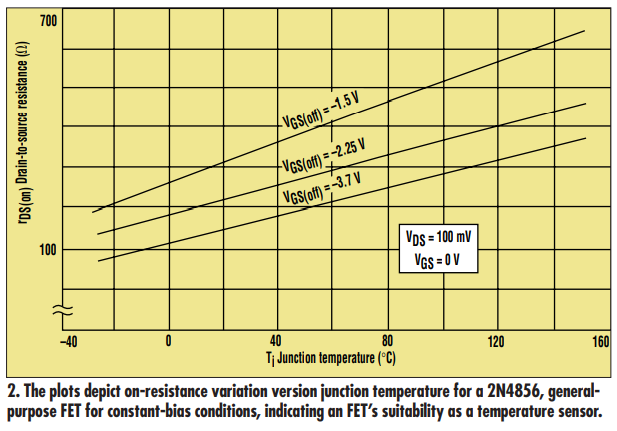
When forward-biased, the transfer
characteristic (VGS vs. Id) of this device exhibits a linear variation of rDS(on), or drain-to-source on-resistance, with the junction temperature
(Tj). This behavior indicates that a
FET could be used as a temperaturesensing resistor (TSR) in the range of
approximately-40°C to +150°C.
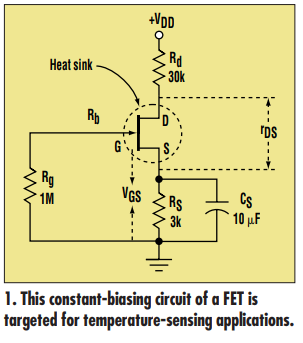
To use a FET as a temperature sensor in a practical application, a metallic
cap preferably made with aluminum
can be used as a heat sink (Fig. 1). The
heat sink senses the temperature bath
and provides linear variation of rDS(on)
with temperature. Increasing junction
temperature causes a linear increase in
drain-to-source on-resistance.
In general usage, junction temperature changes with the mode of operation and biasing configuration of the
FET. But in this application, the biasing and FET operation are kept constant, varying the junction temperature via the heat sink by heating or
cooling above or below room temperature. Compared to N-channel FETS,
P-channel FETS produce a larger variation of rDS(on) over temperature.
The plots given are for Motorola’s
general-purpose N-channel FET
2N4856. Other families of FETs also
exhibit a similar linear response of rDS
with respect to junction temperature.